
Influenza(Flu)
Influenza (Flu)
Influenza is a viral infection affecting the respiratory system, including the nose, throat, and lungs.

Influenza is classified into three main types: Type A, Type B, and Type C.
**Type A influenza** is known for causing more severe illness and complications compared to other types of influenza.
Symptoms of Type A influenza may include fever, headache, muscle aches, sore throat, cough, and in some cases, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Typically, recovery occurs within 5-7 days.
General Symptoms of Influenza
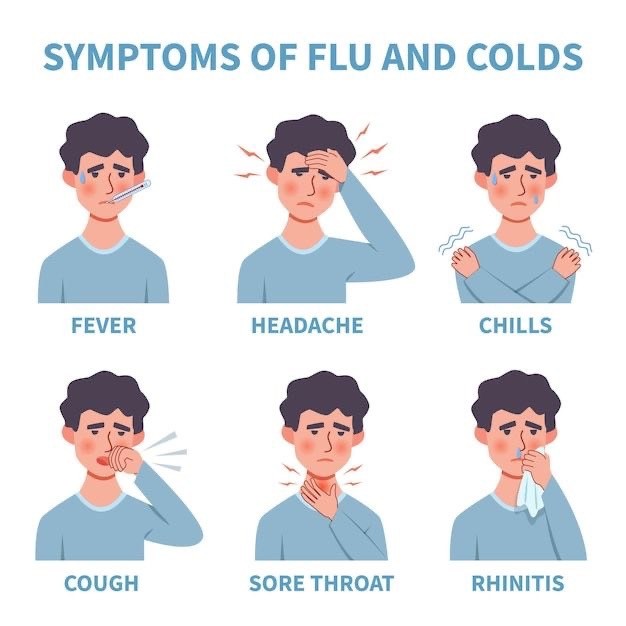
- Fever, chills, and sweating
- Headache and muscle aches
- Sore throat and dry cough
- Eye pain
- Runny nose and sneezing
- Rapid breathing
- Diarrhea and vomiting, which are more common in children
Causes of Influenza
The virus is transmitted through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Others may inhale the virus or touch surfaces contaminated with the virus.
An infected person can spread the virus from 1 day before showing symptoms and continue to be contagious for up to 5 days after symptoms appear. Individuals with weakened immune systems may be contagious for a longer period.
New strains of influenza virus continuously emerge. If vaccinated or previously infected, the body usually has some immunity. If the new strain is similar to a previous one, existing antibodies may offer protection or reduce severity. However, antibody levels decrease over time.
If exposed to a completely new influenza strain, existing antibodies may not be effective in fighting off or preventing the infection.
Treatment for Influenza
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, such as using fever reducers, decongestants, cough medicine, and expectorants. Oral rehydration solutions are recommended for those with diarrhea, reduced food intake, or fatigue. Vitamins and herbal supplements can support the immune system. Rest and increased fluid intake help alleviate influenza symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Most people with influenza can recover at home. However, seek medical attention if
- You experience chest pain or difficulty breathing
- You feel dizzy or faint
- You have seizures
- You experience severe muscle weakness or pain
- Chronic health conditions worsen or deteriorate
Individuals at risk for complications should see a doctor immediately. Antiviral medications can help recover faster and prevent severe symptoms.
Home Care
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as fruit juices, water, or warm soups, to stay hydrated.
- Rest and sleep adequately to help your immune system fight off the virus effectively.

.png)
.png)
.png)




-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)
-250x400.png)




-262x334.jpg)








